









|


In collaboration with the University of Nevada, Reno in USA and National
Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience, the shake
table experiments on a base-isolated building were conducted to evaluate
the effectiveness of seismic isolation technology. Specimen was a five-story
steel building and isolation devices were installed at the base of the
specimen. In the experiment, two different types of isolation system were
used; 1) nine triple-pendulum bearings and 2) combination of five lead-rubber
bearings and four cross linear sliders. Base-fixed specimen also excited
to compare response of the specimen and behavior of furniture installed
in the specimen. The record observed at K-NET Iwanuma station during the
2011 Off the Pacific coast of Tohoku earthquake was imposed.
Duration of this record is about three minutes and it affects various structures
because it contains long-period components, which resonate with base-isolated
buildings, and short-period components, which affects low to middle height
base-fixed buildings.
Outline of the experiment: (20110818.pdf)
Test date: August 18, 26, and 31, 2011
Imposed ground motions: Iwanuma record, K-NET (the 2011 off the Pacific
Coast of Tohoku Earthquake) 70% and 100%
Video: (201108_e.wmv)
|



A series of full-scale shaking experiments on a precast and post-tensioned
concrete (PPC) structure were conducted to establish high-quake-resistant,
productive and reparable concrete buildings. And also experiments on a reinforced concrete (RC) structure with almost the same shape of the
PPC structure were conducted to acquire usable data for the future development
of seismic design method.
In the experiments, both of the PPC structure and the RC structure were
shaken at the same time (the PPC structure at the front and the RC structure
at the back of the video). As for the two 4-story buildings, the story
height of each floor was 3.0 m, and the long side of the rectangular plane
was 14.4 m and the short side was 7.2 m.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (2101213.pdf)
Test date: December 13, 2010
Imposed ground motions: JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 50%
Video: (20101213_jmak50_pc.wmv)
|



Shaking
experiments of damage free reinforced concrete bridge pier were
conducted at E-Defense.
The bridge pier specimen was designed based on the current design
specifications, however, the specimen had two special attributes, one was a new
material, polypropylene fiber mixed reinforced cementitious composite, used to
enhance the ductility capacity of the pier base where the severe damage occurs
under strong excitation and the other was 0.4 m round corners in a square
cross-section of the pier specimen.
The pier specimen was 7.5 m tall and its foundation
was 7.0 m long, 7.0 m wide and 1.8 m tall. Weight of superstructure was 310
tons. Shaking experiments were conducted for three days. The specimen was subjected to JR Takatori record (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) with varying amplitude.
Small cracks were found at the base
of the pier specimen after design level excitation,
which was expected result. After that the specimen was excited twice same as
before simulating aftershocks, it developed large crack but covering concrete
of the new material did not spall off. It was clarified that damage free bridge
pier with the new material enhanced seismic performance.
Outline of the experiment is shown here:(20100226.pdf)
Day 2
Test date:
February 26, 2010
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake)
1st excitation:
JR Takatori record 100%
2nd excitation:
JR Takatori record 100% (20100226_100.wmv)
/ (20100226_sw.wmv)
Day 3
Test date:
March 2, 2010
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) with varying amplitude
1st excitation:
JR Takatori 100%
2nd
excitation: JR Takatori 125%
3rd
excitation: JR Takatori 125%
4th
excitation: JR Takatori 125% (20100302_n.wmv)
/ (20100302_sw.wmv)
|



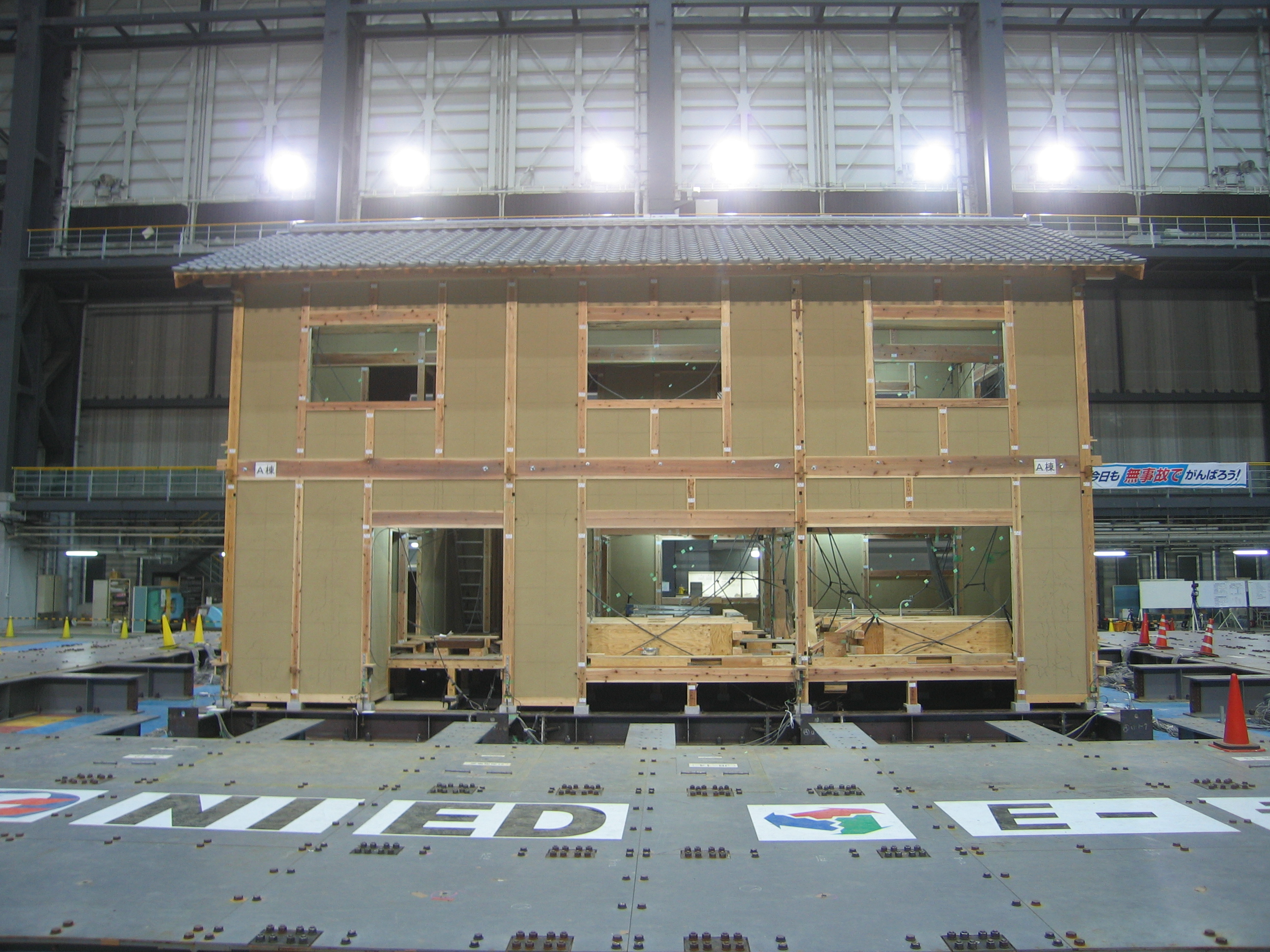
NIED and the Council to Promote Wood Oriented Architecture conducted collapse
experiments to verify the design method for 3-story Wood Houses by Post
and Beam conventional Japanese wood houses under the support of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and
Tourism.
There were two specimens (specimen 1, specimen 2), both of
which were 3-story
wood houses with the same specifications including floor area and height of
each floor except design of joint parts. In the experiment, damage and behavior
of specimens under strong earthquake were confirmed by inputting a synthetic
ground motion in one direction.
Outline
of the experiment is shown here: (20091027.pdf)
Test date: October 27, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion 160%
Panoramic view of back side (20091027.wmv)
|



The test
structure was designed to reproduce the seismic response of an 80-m-tall,
21-story building. The lower four stories of the test structure were
constructed as an actual steel frame. Substitute layers, which consisted of
concrete slabs and rubber bearings, were placed above the steel frame to
simulate the 5th to 21st floors of the building. The structure was subjected to
a series of synthetic long-period ground motions: one for Tokyo from a scenario
Tokai earthquake and another for Nagoya from a scenario Tokai-Tonankai
earthquake.
Outline of the experiment is shown here:
(091223siryou1.pdf) / (091223siryou2.pdf).
Excitation
case 1
Test
date: September 15, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario
Tokai-Tonankai earthquake
Overall
view of test structure (200909_case1-4.wmv)
Steel frames in lower part (200909_case1-12.wmv)
Brace steel damper (200909_case1-19.wmv)
Steel damper in upper substitute layer (200909_case1-24.wmv)
Meeting room on the roof level corresponding to 19th floor (200909_case1-room.wmv)
Excitation
case 2
Test
date: September 18, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario
Tokai-Tonankai earthquake
Overall
view of test structure (200909_case2-4.wmv)
Steel frames in lower part (200909_case2-12.wmv)
Brace steel damper (200909_case2-19.wmv)
Meeting room on roof level corresponding to 19th floor (200909_case2-room.wmv)
Excitation
case 3
Test date:
September 25, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario
Tokai-Tonankai earthquake
Overall
view of test structure (200909_case3-4.wmv)
Steel frames in lower part (200909_case3-12.wmv)
Oil brace damper (200909_case3-19.wmv)
Office room on roof level corresponding to 19th floor (200909_case3-room.wmv)
Excitation
case 4
Test
date: October 2, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario
Tokai-Tonankai earthquake
Overall
view of test structure (200909_case4-4.wmv)
Dining room on roof level
corresponding to 19th floor (200909_case4-room.wmv)
|
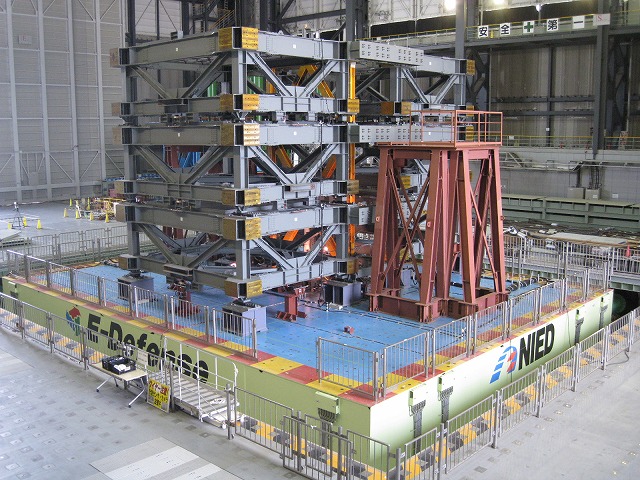



This experiment was conducted under the international collaborative research
agreement between NIED and the George
E. Brown, Jr. Network for Earthquake Engineering Simulation (NEES). Participants comprised US researchers
from Stanford University and the University of Illinois and Japanese
researchers from NIED, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Hokkaido University, and
the private sector.
The objective of the experiment was to evaluate the dynamic properties of a new structural system named the Controlled-Rocking
Frame. The study focused on the self-centering mechanism of the system and the performance of the energy absorbing devices. The
test specimen is seen in the video as a two-dimensional frame painted in yellow.
Six horizontal-mass devices referred to as testbeds, three of which piled up on
each side of the test structure, delivered inertia to the specimen. The specimen was subjected to unidirectional motions
(JMA Kobe and Northridge record) with varying amplitude.
Outline
of the experiment is shown here:(20090819.pdf)
Test date: August 10, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 65%
FUSE-A1 (20090810A1.wmv)
Relevant sites in NEES:
http://cee-neesmrit1.cee.illinois.edu/controlledRockingWebsite/trunk/Index.php
|
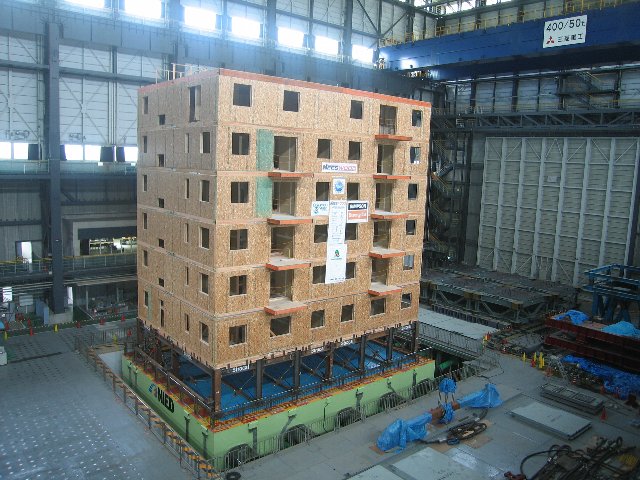



As a part of international collaborative research of NIED and the George E. Brown, Jr. Network for Earthquake
Engineering Simulation (NEES), a shaking table experiment on a full-scale 7-story wood building was conducted
by NEESWood, which is responsible for study in wood structure at NEES, (PI:
Professor John W. van de Lindt, Colorado State University) and NIED. The first
story of the test structure was a steel frame simulating a basement parking
area. The 2nd to 7th stories were the residential area constructed by the
wood-frame structure. The test structure was 12.4 m wide, 18.4 m long and 20.4 m
high. In the experiment, the seismic motion recorded at Canoga Park during 1994
Northridge earthquake was used. The test structure was shaken by the 180% of
the seismic motion, and the response of the structure under the severe input
motion was investigated.
Outline
of the experiment is shown here: (20090714.pdf)
Test date:
July 14, 2009
Imposed
ground motions: Canoga Park
record (1994 Northridge earthquake) 180%
Panoramic
view from obliquely upward (20090714_1.wmv)
Inside of a room on the 7th floor (20090714_2.wmv)
|



The performance enhancement by damping devices was examined in a full-scale,
5-story, steel moment-resisting frame building. Validation of supplemental
damping systems was needed because these systems have never been exposed
to a major earthquake event. The building was tested under five conditions:
with steel, viscous, oil, and viscoelastic dampers, and without dampers.
Nonstructural elements (cladding, ceiling, partition walls) were installed
to simulate a realistic office building. The JR Takatori record was used
with various amplitudes.
Outline
of the experiment is shown here: (20090305.pdf)
Test
date: March 5, 2010
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%,
Steel damper (20090305.wmv)
Test
date: March 12, 2010
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Viscous damper (20090312.wmv)
Test
date: March 19, 2010
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Oil damper (20090319.wmv)
Test
date: March 27, 2010
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Viscoelastic damper (20090327.wmv)
|


 |
| The total view of the specimen |
Shaking table experiments
had been conducted to evaluate ability of functional maintenance of medical
facilities under earthquake disaster.
A full-scale 4-story
reinforced concrete building specimen simulating a hospital which contained a
stuff station, a dialysis room, an operating
room and a patient’s room each furnished with real medical equipment and
furniture was set up to reproduce function of the medical facility more
faithfully.
Two hospitals of
different kind of structure each, one for a base-fixed structure and the other
for a seismic isolated structure, were compared and evaluated their functional
maintenance by shaking table experiments. Comparative video of the experiments shows
risk of the aseismic hospital and ability of functional maintenance of the
seismic isolated hospital under a near fault earthquake ground motion.
But even a seismic isolated
structure which widely reduces damages against earthquake in general can be
exposed to risk by long-period, long-duration earthquake ground motion such as synthetic ground motion for
Sannomaru area, Nagoya from a scenario Tokai-Tonankai earthquake if one fails to take earthquake countermeasures.
Results of the experiments
are going to be used to upgrade ability of functional maintenance of medical
facilities in the future.
 |
| The movement of the unlocked rollaway bed |
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20081225.pdf)
Test
Date: December 2008 & January 2009
Imposed ground motion:
(1) JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 80%, near fault earthquake,
(2) Synthetic ground motion for Sannnomaru area, Nagoya from a scenario
Tokai-Tonankai earthquake
Comparative
video of aseismic and a seismic isolation structure (20090122.wmv)
 |

|
NIED and Japan Housing and Wood Technology Center had conducted shaking
table experiments on creation of design method and performance validation
project of Traditional Wooden Houses under the support of Ministry of Land,
Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
There were
two test specimens (House A and B) in this experiment. They were two 2-story wood-framed
houses built in a traditional manner. The modules and floor area and height of
each story were not the same for both specimens but the floor plans were almost
the same. In the experiment, by inputting a ground motion such as observed
ground motion of the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake, damage and behavior of the
specimens under strong earthquake were confirmed.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20081128.pdf)
Report of outcome (to external site)
|
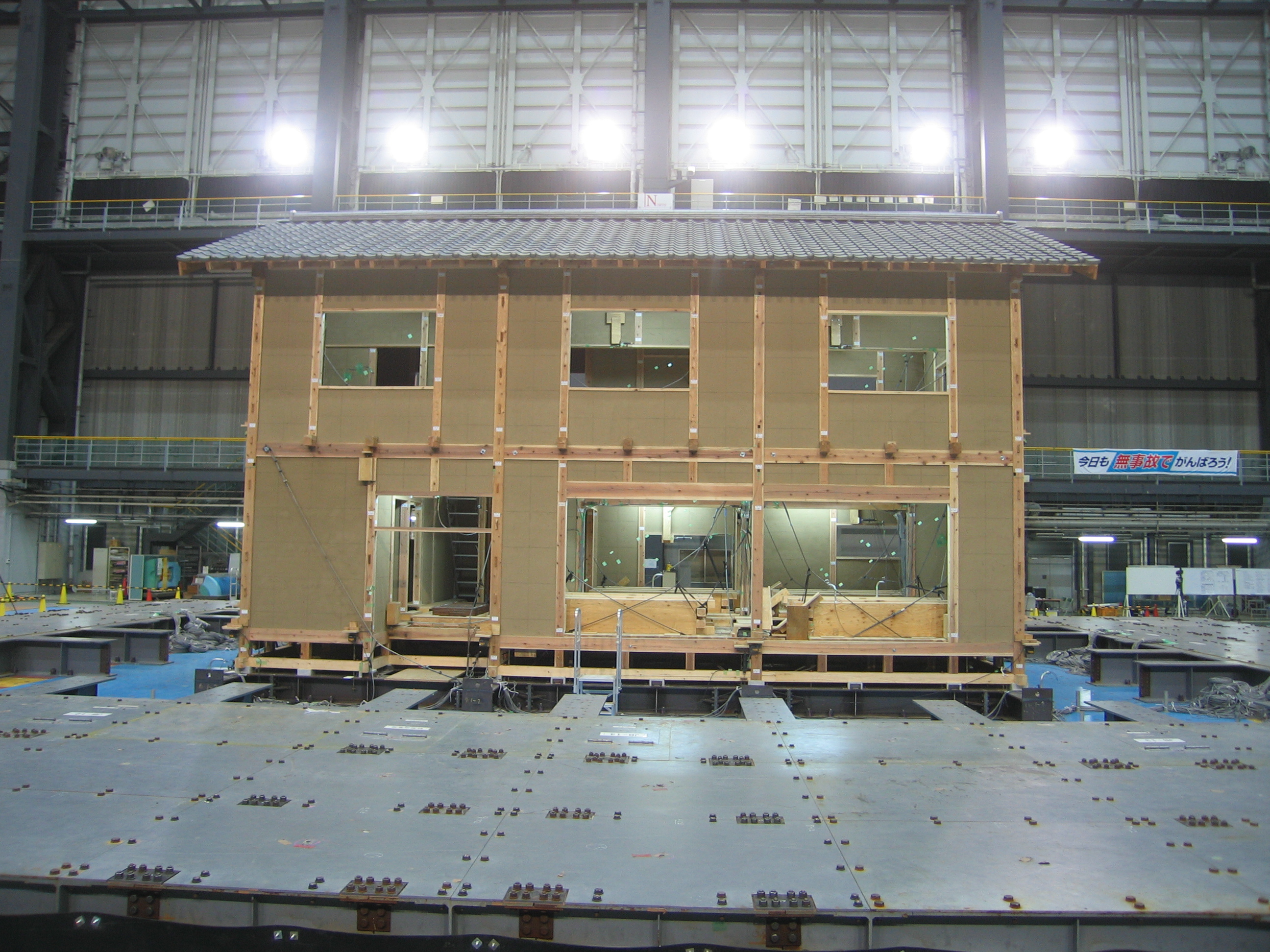 |
| House B |
 |
| House A |
Test date:
November 28, 2009
Imposed
ground motion: JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Panoramic
view from front side of House B (20081128.wmv)
Test date:
December 4, 2009
Imposed
ground motion: JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Panoramic
view from front side of House A (20081204.wmv)
|



A shake table experiment of
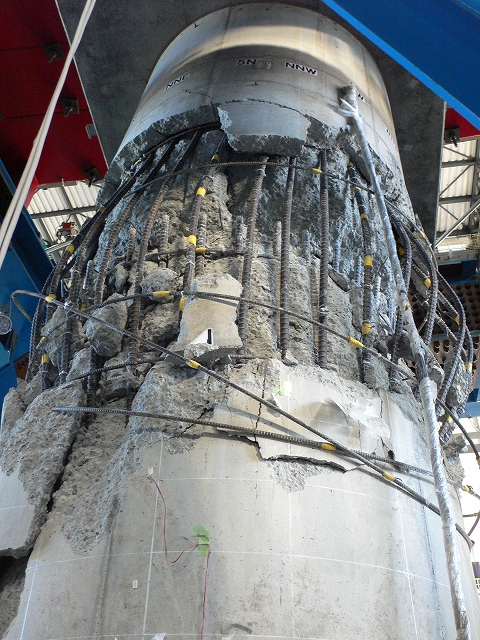
full-scale RC bridge pier was conducted.The pier was designed as a
reinforced concrete bridge column which built in 1970’s and it had termination
of longitudinal bars at the mid-height of the pier. The pier had a circular
section with a diameter of 1.8 m and the height of the pier was 7.5 m. Its
foundation was 7.0 m by 7.0 m and 1.8 m tall. The weight of superstructure was
about 300 tonf.
Based on
the experiment, progress of the damage, which is similar with the damage of the
reinforced concrete piers collapsed during the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake,
was reproduced and taken its data.
Test data Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20081002.pdf)
Test date: October 2, 2008
Imposed ground motion: JR Takatori record (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20081002.wmv)

|
 A shake table experiment of full-scale RC bridge pier was conducted. A shake table experiment of full-scale RC bridge pier was conducted.
The pier was designed as a reinforced concrete bridge pier based on the current designed code and it had a circular section with a diameter of 2.0m and the height of the pier was 7.5m. Its foundation was 7.0m by 7.0m and 1.8m tall. Weight of superstructure was about 310t. The pier was excited for 2 days.
As the result, it was found that the reinforced concrete bridge pier based
on current design code has enough ductility capacity for 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu
Earthquake.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20080826.pdf) / (20080902.pdf)
Test date:
August 26, 2008
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake)
1st excitation : JR Takatori 100%
2nd excitation : JR Takatori 100% (20080826.wmv)
Test date:
September 2, 2008
Imposed ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake)
with varying amplitude
1st excitation: JR Takatori 100%
2nd excitation: JR Takatori 125%
3rd excitation: JR Takatori 125% (20080902.wmv)
|


|
 A test structure to
investigate the seismic performance of high-rise steel buildings represented a
21-story and 80-m-tall building corresponding to average high-rise buildings.
The test structure was comprised of the lower part of full-scale 4-story steel
frame structure and the higher part of substitute layers. The substitute layers
were prepared in order to represent the seismic responses generated in 5th to
21st floors of the model building. The steel frame was designed and constructed
in reference to the past design materials. Imposed ground motions were a synthetic ground motion for simulating the metropolitan area from a scenario Tokai earthquake and a synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario Tokai-Tonankai
earthquake A test structure to
investigate the seismic performance of high-rise steel buildings represented a
21-story and 80-m-tall building corresponding to average high-rise buildings.
The test structure was comprised of the lower part of full-scale 4-story steel
frame structure and the higher part of substitute layers. The substitute layers
were prepared in order to represent the seismic responses generated in 5th to
21st floors of the model building. The steel frame was designed and constructed
in reference to the past design materials. Imposed ground motions were a synthetic ground motion for simulating the metropolitan area from a scenario Tokai earthquake and a synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario Tokai-Tonankai
earthquake
Outline
of the experiment is shown here: (20080321.pdf)
Test date:
March21, 2008
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario
Tokai-Tonankai earthquake
Panoramic
view (front) (20080321_w11.wmv)
Panoramic
view (skew) (20080321_w22.wmv)
Joint, bond part, member (20080321_w33.wmv)
|


|
 A large-amplitude floor
response of a high-rise building was reproduced by using 5-story steel frame
test structure with two amplifying layers comprised of rubber bearings and
concrete slab. A large-amplitude floor
response of a high-rise building was reproduced by using 5-story steel frame
test structure with two amplifying layers comprised of rubber bearings and
concrete slab.
Realistic conditions of
residential room as well as office room were reproduced and a tuned synthetic ground
motion was input to the shaking table. The large-amplitude floor response
corresponding to the maximum displacement of 1.5 m was reproduced in the test
structure of 5-story frame. The response of the test structure was tuned to
represent the floor response of the 30th floor of a 30-story high-rise building
which was subjected to synthetic
ground motion for Nagoya from a scenario Tokai-Tonankai earthquake. Dangerous phenomena in the office room, residential room, kitchen and
living room were clarified and the resistant measure prepared in the same
type of rooms showed significant improvement in terms of safety.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20080124.pdf)
Conclusion paper is shown here: (20080124_kenkyusiryou.pdf)
Test date:
January24, 2008
Imposed
ground motions: Synthetic ground motion from a scenario Nankai earthquake
Video: (20080124_t1.wmv)
|


|
 A shake table experiment of full-scale reinforced concrete bridge pier designed based on 1968 technical criteria was conducted to clarify the failure mechanism which occurred during 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake. In the experiment, the ground motion recorded at JR Takatori station during 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake was imposed. A shake table experiment of full-scale reinforced concrete bridge pier designed based on 1968 technical criteria was conducted to clarify the failure mechanism which occurred during 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake. In the experiment, the ground motion recorded at JR Takatori station during 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake was imposed.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20071213.pdf)
Test date:
December 13, 2007
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20071213.wmv)
|


|
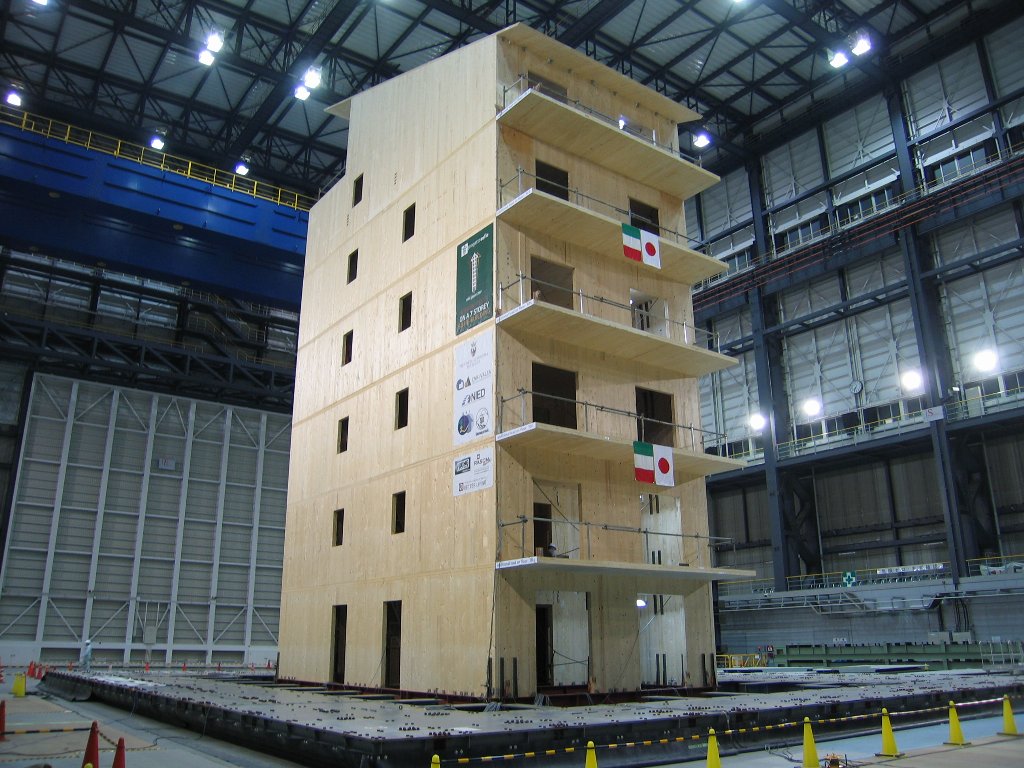 As a part
of international collaborative research of NIED and
CNR-IVALSA “Istituto per la Valorizzazione del Legno e delle Specie Arboree-Trees and Timber
Institute - Firenze ITALY”, a shaking experiment of full-scale 7-story wood structure was
conducted. This was a part of SOFIE project, PI : Professor Ario Ceccotti,
which was CNR-IVALSA leading project to develop the construction method by
cross laminate panel, XLam: 7 cm to 20 cm thick laminated panel made of 2 cm
thick piece of wood bonded alternately and thickly without any interspace. As a part
of international collaborative research of NIED and
CNR-IVALSA “Istituto per la Valorizzazione del Legno e delle Specie Arboree-Trees and Timber
Institute - Firenze ITALY”, a shaking experiment of full-scale 7-story wood structure was
conducted. This was a part of SOFIE project, PI : Professor Ario Ceccotti,
which was CNR-IVALSA leading project to develop the construction method by
cross laminate panel, XLam: 7 cm to 20 cm thick laminated panel made of 2 cm
thick piece of wood bonded alternately and thickly without any interspace.
A test
structure was timber box-frame construction which was 23.5 m height, 7.5 m
width, 15 m depth and total weight 285 tonf. The test structure was shaken by
the JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake), and the response of the
structure under the severe motion was investigated.
Test date:
October 23, 2007
Imposed
ground motions: JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Panoramic
view (skew) (20071023 1.wmv)
7F (inside of the room)(20071023_2.wmv)
|


|
 A full-scale 4-story steel building was repeatedly subjected to ground
shaking until it collapsed. The building satisfied the minimum requirements
prescribed in the current Building Standard Law of Japan. Composite concrete
slabs were provided to complete a very realistic structure. The building
was furnished with a complete set of nonstructural elements including ALC
(AAC) exterior walls, aluminum sash, glass windows, partition walls, and
ceiling. The experiment was conducted by increasing the intensity of excitation
gradually from small to the strongest motion that the E-Defense can produce. A full-scale 4-story steel building was repeatedly subjected to ground
shaking until it collapsed. The building satisfied the minimum requirements
prescribed in the current Building Standard Law of Japan. Composite concrete
slabs were provided to complete a very realistic structure. The building
was furnished with a complete set of nonstructural elements including ALC
(AAC) exterior walls, aluminum sash, glass windows, partition walls, and
ceiling. The experiment was conducted by increasing the intensity of excitation
gradually from small to the strongest motion that the E-Defense can produce.
Outline
of the experiment is shown here: (20070927.pdf)
Test date:
September 25, 2007
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu
Earthquake) 40%
Video: (20070925.wmv)
Test date:
September 27, 2007
Imposed
ground motions: JR Takatori record (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20070927.wmv)
|


|
 A full-scale test
structure which was partially extracted from a high-rise building was shaken to
reproduce the floor response and story drift. The experiment was conducted in
order to clarify those phenomena which may occur in and outside of high-rise
buildings under a long-period ground motion. Damage of nonstructural components
including exterior wall and ceiling as well as dangerous behavior including
overturning and scattering of fixtures and fittings were observed in the test
structure. Adopted earthquakes were Nankai earthquake expected in near future
and the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu earthquake. A full-scale test
structure which was partially extracted from a high-rise building was shaken to
reproduce the floor response and story drift. The experiment was conducted in
order to clarify those phenomena which may occur in and outside of high-rise
buildings under a long-period ground motion. Damage of nonstructural components
including exterior wall and ceiling as well as dangerous behavior including
overturning and scattering of fixtures and fittings were observed in the test
structure. Adopted earthquakes were Nankai earthquake expected in near future
and the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu earthquake.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20070329.pdf)
Test date:
March 29, 2007
Imposed ground
motions: Synthetic ground motion from a scenario Nankai earthquake (continued period:
180 seconds)
Video: (20070329.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a collapse experiment of
full-scale wooden houses was conducted. 2 test structures, house C and D whose
framework were the same of house A and B tested in November 2005, were built
newly. The test structures were constructed based on the previous building
standards which were used until 1981 and whose seismic performance was
insufficient. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a collapse experiment of
full-scale wooden houses was conducted. 2 test structures, house C and D whose
framework were the same of house A and B tested in November 2005, were built
newly. The test structures were constructed based on the previous building
standards which were used until 1981 and whose seismic performance was
insufficient.
The purpose of the experiment on House C was to investigate the effect
of aging on the seismic capacity of wooden house. The purpose of the experiment
on House D was to verify the effect of partial seismic reinforcement compared
with House B which was considered to be fully reinforced, specifically
the lack of the reinforcement at joints.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20070228.pdf)
Test date:
February 28, 2007
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu
Earthquake) 100%
1st excitation: JR Takatori 100% (20070228_1.wmv)
2nd excitation: JR Takatori 100% (20070228_2.wmv)
Test date:
March 5, 2007
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu
Earthquake) 100%
4th excitation: JR Takatori 100% (20070305_4.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), an experiment of full-scale
wooden houses built by traditional timber framework method was conducted. The method
of the test structures were used to be common before 1950, in which the
Japanese Building Standard Law was enacted, and those structures have aseismic
elements whose behavior of performance at seismic events were not yet
clarified. We focused attention on difference of foundation style, floor
stiffness and roof style, and conducted experiments on eccentricity ratio,
floor stiffness, roof style and column base style as parameters to validate
their impact to aseismic capacity of houses. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), an experiment of full-scale
wooden houses built by traditional timber framework method was conducted. The method
of the test structures were used to be common before 1950, in which the
Japanese Building Standard Law was enacted, and those structures have aseismic
elements whose behavior of performance at seismic events were not yet
clarified. We focused attention on difference of foundation style, floor
stiffness and roof style, and conducted experiments on eccentricity ratio,
floor stiffness, roof style and column base style as parameters to validate
their impact to aseismic capacity of houses.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20070130.pdf)
Test date:
February 2, 2007
Imposed ground
motions: JMA Kobe recorded (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video:(20070202.wmv)
|



As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas”
supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
(MEXT), a
shaking experiment was conducted with a large-scale model composed of caisson
type quay walls and pile group in order to perceive lateral spreading
phenomenon of the ground induced by liquefaction in coastal areas. About 900
channel sensors were set to clarify ground behavior and failure process of the
pile foundation when lateral spreading occurred. Large displacements of the
ground and the structures, and significant change of earth pressure and pore
water pressure were captured by the sensors.
Test date:
December 15, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 80%
Direction of shaking: horizontal 1 direction
and vertical direction
Video: (20061215.wmv)
|


|
 As a part of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban
Areas,” supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science
and Technology (MEXT), shaking table experiments of 3-story reinforced
concrete (RC) school buildings was conducted under the leadership of Prof.
Toshimi Kabeyasawa of Earthquake Research Institute, the University of Tokyo. The
main objectives were to validate input dissipation and seismic retrofit
effect. The test specimens were two 3-story RC building structures. One
was a bare RC specimen, simulating an old and non-ductile school building.
The other was a retrofit specimen, which was constructed in the exactly
same design as the bare RC specimen but strengthened with attached steel
braces. Those test structures were constructed on a pool-shaped container
each which were simulating the flexible boundary condition of the spread
foundation and neighborhood soils. As a part of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban
Areas,” supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science
and Technology (MEXT), shaking table experiments of 3-story reinforced
concrete (RC) school buildings was conducted under the leadership of Prof.
Toshimi Kabeyasawa of Earthquake Research Institute, the University of Tokyo. The
main objectives were to validate input dissipation and seismic retrofit
effect. The test specimens were two 3-story RC building structures. One
was a bare RC specimen, simulating an old and non-ductile school building.
The other was a retrofit specimen, which was constructed in the exactly
same design as the bare RC specimen but strengthened with attached steel
braces. Those test structures were constructed on a pool-shaped container
each which were simulating the flexible boundary condition of the spread
foundation and neighborhood soils.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20061002.pdf)
(Bare specimen)
Test date:
October 2, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JMA Kobe record (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20060930.wmv)
(Retrofit specimen)
Test date:
November 1, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JMA Kobe record (1995
Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 130%
Video: (20061030.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas”
supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
(MEXT), a
series of shaking experiments on pile foundation placed in level liquefiable
ground had been conducted by using a cylindrical laminar container to examine
behavior of liquefied ground and structural interaction in consequence of
shaking. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas”
supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
(MEXT), a
series of shaking experiments on pile foundation placed in level liquefiable
ground had been conducted by using a cylindrical laminar container to examine
behavior of liquefied ground and structural interaction in consequence of
shaking.
Test date:
August 25, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 50%
Direction of shaking: horizontal 2 directions
Video: (20060825.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a series of shaking experiments
was conducted to comprehend lateral spreading phenomena of the ground induced
by liquefaction of coastal areas using a large-scale specimen with sheet pile
type quay wall and pile group foundation structure. About 900 channel sensors
were set in order to clarify ground behavior of lateral spreading and failure
process of pile foundation structure under earthquakes. As a result, large
displacement of the ground and the structures, and significant change in earth
pressure and pore water pressure were observed through the sensors. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a series of shaking experiments
was conducted to comprehend lateral spreading phenomena of the ground induced
by liquefaction of coastal areas using a large-scale specimen with sheet pile
type quay wall and pile group foundation structure. About 900 channel sensors
were set in order to clarify ground behavior of lateral spreading and failure
process of pile foundation structure under earthquakes. As a result, large
displacement of the ground and the structures, and significant change in earth
pressure and pore water pressure were observed through the sensors.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20060323.pdf)
Test date:
March 23, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 80%
Direction of shaking: horizontal 1 direction
and vertical direction
Video: (20060323.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a series of shaking experiments
on soil-pile foundation interaction was conducted. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a series of shaking experiments
on soil-pile foundation interaction was conducted.
Test date:
February 24, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 80%
Video: (20060224.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas,” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a shaking table experiment of
full-scale 6-story reinforced concrete (RC) building had been conducted. The
test specimen was 12 m long, 17 m wide, 16 m tall, 6-story building and its
weight was around 1,000 tonf which was the heaviest test structure ever since
E-Defense started running. The structure was designed based on the code of
design and practice in 1970’s. The test specimen was subjected to the record of
the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake and the behavior was studied to obtain
necessary data for upgrading earthquake-resistance improvement technology of RC
building. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas,” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), a shaking table experiment of
full-scale 6-story reinforced concrete (RC) building had been conducted. The
test specimen was 12 m long, 17 m wide, 16 m tall, 6-story building and its
weight was around 1,000 tonf which was the heaviest test structure ever since
E-Defense started running. The structure was designed based on the code of
design and practice in 1970’s. The test specimen was subjected to the record of
the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake and the behavior was studied to obtain
necessary data for upgrading earthquake-resistance improvement technology of RC
building.
Outline of the experimental is shown here: (20060110.pdf)
Test date: January 13, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JMA Kobe (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20060113.wmv)
Test date:
January 16, 2006
Imposed ground
motions: JMA Kobe (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 60%
Video: (20060116.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), shaking experiment of full-scale
wooden houses built before 1981, when the Building Standard Law was revised
drastically, was conducted. The test structures were two similar houses chosen
by public offering, relocated from Nishiakashi city to E-Defense. Then one was left
as it was (House B) and the other was reinforced against earthquake (House A).
Both of test structures were shaken at the same time and investigated the
differences of their behavior under a large earthquake. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), shaking experiment of full-scale
wooden houses built before 1981, when the Building Standard Law was revised
drastically, was conducted. The test structures were two similar houses chosen
by public offering, relocated from Nishiakashi city to E-Defense. Then one was left
as it was (House B) and the other was reinforced against earthquake (House A).
Both of test structures were shaken at the same time and investigated the
differences of their behavior under a large earthquake.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20051121.pdf)
Remind: The seismic performance scores by the precise seismic diagnosis
in the experiment outline (20051121.pdf) are modified after the experiment.
See the document (20140602.pdf) for the detail.
Test date: November 21, 2005
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20051121.wmv)
Test date:
November 24, 2005
Imposed ground
motions: JR Takatori record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake) 100%
Video: (20051124.wmv)
|


|
 As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), shaking experiment on full-scale
wooden houses built before WWII was conducted. For their oldness, severe damage
is concerned at a large earthquake. The two test structures, one for an actual
built house relocated from Kyoto city and the other for a house newly designed
and built in the similar timber frame method as one relocated from Kyoto based
on new design method were shaken at the same time to clarify their
earthquake-resisting capacity. As a part
of “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas” supported
by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), shaking experiment on full-scale
wooden houses built before WWII was conducted. For their oldness, severe damage
is concerned at a large earthquake. The two test structures, one for an actual
built house relocated from Kyoto city and the other for a house newly designed
and built in the similar timber frame method as one relocated from Kyoto based
on new design method were shaken at the same time to clarify their
earthquake-resisting capacity.
Outline of the experiment is shown here: (20051110.pdf)
Test date:
November 10, 2005
Imposed ground
motions: Building Center of Japan Level 2 Seismic Wave (BCJ-L2), unilateral excitation with peak acceleration of 400 gal
Video: (20051110_1.wmv)
Test date:
November 11, 2005
Imposed ground
motions: JMA Kobe record (1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu
Earthquake) 100%
Video:(20051110_2.wmv)
|

|



