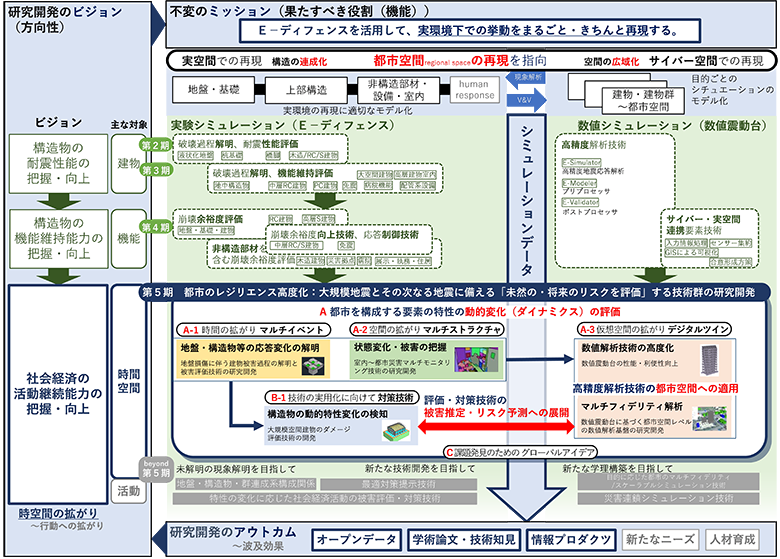
Research and development for resilience enhancement in regional areas with E-Defense and research infrastructure
From structures to regional areas, potential of E-Defense to protect our way of life
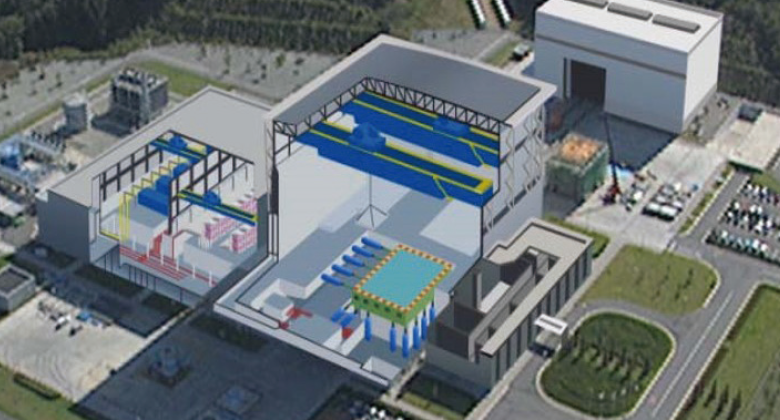

Department of Urban Disaster Resilience Engineering is working on research and development mainly using E-Defense, one of the world's largest testing facilities. E-Defense was developed in the aftermath of the 1995 Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Disaster, which caused devastating loss of life and property due to collapsed structures; NIED began its operation upon the construction completion in 2005.
In the beginning of its operation, we have conducted E-Defense experiments for research on evaluating the collapse mechanism and effectiveness of countermeasures technologies, as well as developing numerical simulation technology to analyze building damage in detail.
We also worked on research and development related to maintaining the functionality of buildings. Buildings have various functions, such as housing, offices, hospitals, and schools. We conducted an experiment to confirm whether the building could withstand a major earthquake and maintain its functionality even after the quake, and to what extent it would withstand.
Developing these achievements, in the next phase, with a new vision of “Contributing to the evaluation and improvement of the socio-economic sustainability performance,” we are working on research and development of technology for damage estimation and risk forecasting in regional areas, in order to realize a resilient society that can continue our activities reliably even after an earthquake.
World's largest three-dimensional shaking table: 3-D Full-Scale Earthquake Testing Facility (E-Defense)
-
-
E-Defense is an experimental facility located in Miki City, Hyogo Prefecture, that can carry out shaking table tests on full-scale structures using the world's largest and most powerful shaking table (20m x 15m, maximum load capacity 1,200t).

-
Research and development cases utilizing E-Defense
We have conducted a wide range of research on individual buildings, including the reproduction of earthquakes, evaluation of building seismic performance, verification of earthquake retrofitting methods and real-time health monitoring technologies, and research on the functionality maintenance of building. This experimental facility is also a shared experimental facility that can be used by external organizations. Private companies also use E-Defense for product development and verification.

-
- An experiment to see how much difference there is in earthquake damage between a wooden house built to the old seismic standard (left) and a wooden house reinforced to the current standard (right).

-
- There has been an increase in the number of cases where impermeable sheets are laid inside the embankment of a reservoir to prevent water leakage, and this experiment examined how to lay them to prevent damage from collapse due to earthquakes.

-
- In order to reduce damage caused by furniture and fixtures falling over, we reproduced the damage situation in the rooms and offices and promoted countermeasures based on the results.

There has been a total of 123 E-Defense experiments (as of March 2023), including those conducted independently by NIED and joint research projects with industry, government, academia and the public. With the exception of some closed experiments, the details of these experiments (experiment objectives, building blueprints, sensor locations) and raw data are made public on the Archives of Shaking table Experimentation dataBase and Information (ASEBI).
We also develop VR technology that uses video data from experiments to enable people to experience simulated earthquakes. By combining existing earthquake footage with the simulation technology that we research in this project, we can further deepen people's understanding of earthquake damage.
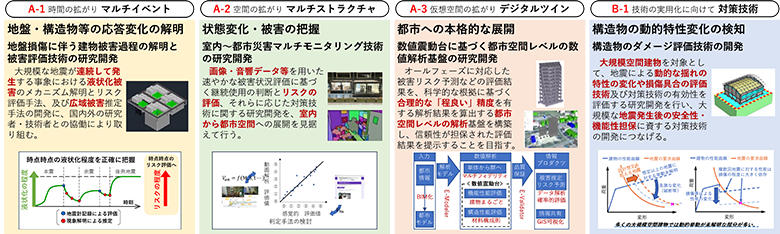
Detection and evaluation of changes in the area; assessment of damage and risk
When expanding the scope of research to include regional areas, it is also important to understand the effects on “buildings” of the interaction through the ground, such as damage to the underground structures, connecting infrastructure, and the impact of adjacent buildings. With E-Defense, this project implements an evidence-based investigation of the influence of the change in ground conditions induced by a large earthquake, such as the future Nankai Trough Earthquake, on the structure.
In addition, to effectively detect the spatial change in space in the building or area in the region caused by an earthquake, the project also works to develop the sensing technology to recognize the conditions through “spatial” data such as footage and acoustics, which will be established based on the results of the E-Defense experiments. The knowledge gained from the project will be applied to damage and risk assessment technologies based on spatial data and resulting information, from the rooms of the buildings to their surroundings, and even to the area in the region.
Furthermore, in order to provide reasonable information for regional damage and risk assessment, the project will develop the “regional level” numerical simulation platform, including “E-Simulator,” which is based on the knowledge gained from E-Defense experiments, as the core technology, and the cyberspace models based on various buildings and soil conditions.
Global promoting of research and development with E-Defense
NIED is promoting the creation of various information products that support people's lives. Our efforts are also aimed at developing technologies that produce information that contributes to the assessment of damage and risk from earthquake disasters.
Since strengthening resilience against earthquake disasters is a common issue in earthquake-prone countries, we think it is necessary to share the results, findings and knowledge gained from E-Defense experiments globally. Under our new vision, it is convinced that finding “global ideas” through discussions among domestic/international researchers and engineers, valuing collaboration and co-creation through the use of E-Defense and promoting research and development for earthquake disaster mitigation.

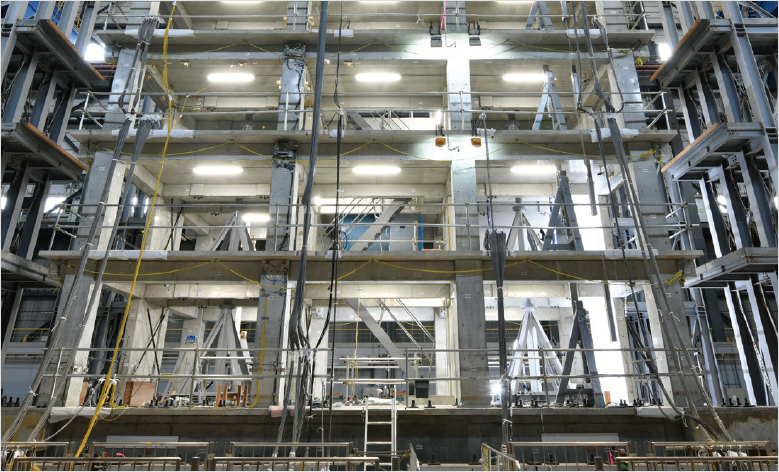
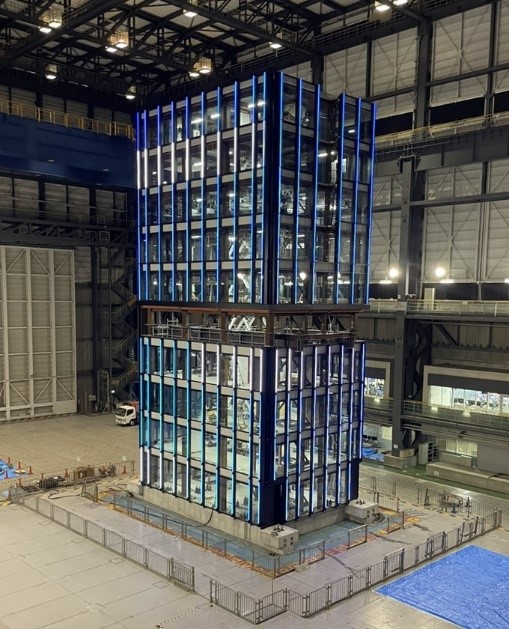
TOPICS: Dynamic property evaluation experiment on a 10-story steel-framed office test structure
In the 10-story steel-frame building experiment conducted in February 2023, the specimen simulates a company office, and exterior materials equipped with LED lighting are installed around its perimeter.
・Developed a method to evaluate building's shaking characteristics (dynamic characteristics) using small and medium-sized earthquakes that occur frequently in Japan, in order to help earthquake countermeasures for actual buildings in society.
・Developed a sensing and optical alert system mounted on building exterior materials to quickly determine the status of a building after an earthquake and whether or not it can continue to be used, even at night.
Dimensions: width 12m, depth 8m, height 27m
Number of floors: 10
Structure: steel frame
Long side: frame with vibration control braces
Short side: pure framed structure
Interior: space utilization by a total of 23 organizations
-
- During normal times

-
- During earthquake
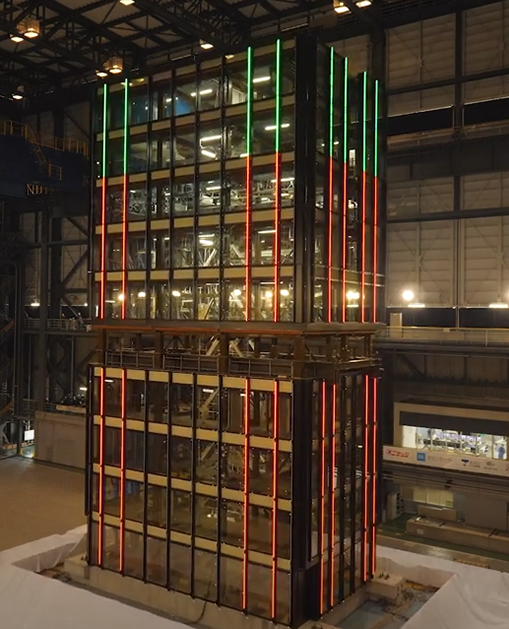

During normal times, the LED lighting installed on the front of the exterior material illuminates, and during earthquakes and disasters, the LED lighting at both ends clearly indicates the deformation of the building observed during the earthquake and whether the building can continue to be used or not, depending on the color of the LED lighting. Specifically, green indicates safety, yellow indicates caution, and red indicates danger.
